Overview¶
Architecture¶
Mirage is divided into four main components :
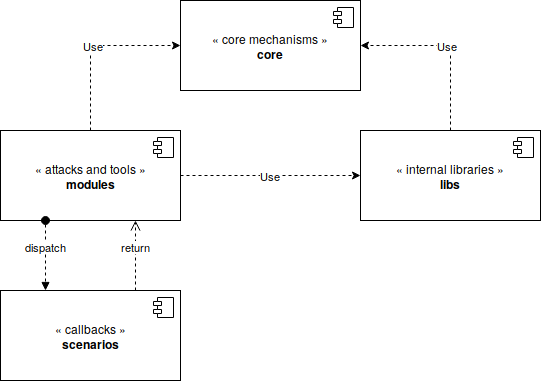
The core component (“core”) : this component includes the core mechanisms of the framework. First, it allows to load, configure and execute the modules. It provides some mechanisms allowing to manipulate background tasks, signals, parameters and configuration files. It provides an unique entrypoint.
The internal libraries (“libs”) : this component is in charge of implementing the Bluetooth Low Energy stack (
mirage.libs.ble). It also provides some display and logging mechanisms (mirage.libs.io) and some utilities and helpers functions (e.g. background tasks manipulation, time management, …).The attacks and tools (“modules”) : these components, called modules, implement the different attack and tools provided by Mirage. They provide a specific attack or function (such as Man-in-the-Middle, sniffing …) and can be used independently or sequentially thanks to the chaining operator.
The callbacks (“scenarios”) : some modules (such as Man-in-the-Middle) implements some complex behaviours and implements a standardised API allowing to easily customize their execution. The scenarios are specialised classes composed of bindings allowing to quickly customize a module’s execution.
Modules¶
One key feature of Mirage is to provide a modular environment for security audits and pentesting. As a consequence, it provides some software components called modules, allowing to perform simple actions or attacks.
Every module uses some input parameters and can generate some output parameters. Inputs and outputs are named (e.g. INTERFACE) and their values are simple strings. These parameters can be easily modified using the command-line interface (CLI) or directly from the bash environment.
The following modules allows to manipulate Bluetooth Low Energy communications :
Name |
Description |
Documentation |
|---|---|---|
ble_info |
This module displays useful informations about a given interface. |
|
ble_connect |
This module connects to a Peripheral’s device as Central. |
|
ble_master |
This module simulates a Central device. |
|
ble_slave |
This module simulates a Peripheral device. |
|
ble_discover |
This module allows to dump the ATT/GATT database of a Peripheral. |
|
ble_adv |
This module sends advertisements. |
|
ble_scan |
This module discovers Advertisers and Peripherals by scanning advertisements. |
|
ble_pair |
This module performs a pairing with a Peripheral or a Central. |
|
ble_mitm |
This module performs a Man-in-the-Middle attack. |
|
ble_sniff |
This module sniffs the advertisements and new / existing connections. |
|
ble_jam |
This module jams the advertisements or connections. |
|
ble_hijack |
This module hijacks an existing connection. |
|
ble_crack |
This module cracks a Temporary Key. |
|
ble_monitor |
This module monitors an HCI communication. |
The following modules allows to manipulate Enhanced ShockBurst communications :
Name |
Description |
Documentation |
|---|---|---|
esb_info |
This module displays useful informations about a given interface. |
|
esb_scan |
This module performs a scan in order to discover Enhanced ShockBurst devices. |
|
esb_sniff |
This module sniffs the Enhanced ShockBurst frames. |
|
esb_inject |
This module allows to inject some Enhanced ShockBurst frames. |
|
esb_ptx |
This module simulates an Enhanced ShockBurst PTX (transmitter). |
|
esb_prx |
This module simulates an Enhanced ShockBurst PRX (receiver). |
|
esb_mitm |
This module performs a Man-in-the-Middle targeting Logitech Unifying devices. |
The following modules allows to manipulate Mosart communications :
Name |
Description |
Documentation |
|---|---|---|
mosart_info |
This module displays useful informations about a given interface. |
|
mosart_scan |
This module performs a scan in order to discover Mosart devices. |
|
mosart_sniff |
This module sniffs the Mosart frames. |
|
mosart_inject |
This module allows to inject some Mosart frames. |
|
mosart_keylogger |
This module analyzes the keystrokes packets transmitted by a Mosart keyboard. |
|
mosart_keyinjector |
This module allows to transmit some keystrokes packets to a Mosart dongle. |
The following modules allows to manipulate WiFi communications :
Name |
Description |
Documentation |
|---|---|---|
wifi_info |
This module displays useful informations about a given interface. |
|
wifi_deauth |
This module performs a deauthentication attack. |
|
wifi_rogueap |
This module creates a basic rogue access point (not connectible). |
|
wifi_scan |
This module discovers Access Points and WiFi stations. |
The following modules allows to manipulate Zigbee communications :
Name |
Description |
Documentation |
|---|---|---|
zigbee_info |
This module displays useful informations on a given interface. |
|
zigbee_deauth |
This module performs a deauthentication attack. |
|
zigbee_floodassoc |
This module performs an association flooding attack. |
|
zigbee_inject |
This module allows to inject some Zigbee frames. |
|
zigbee_scan |
This module scans for Zigbee devices on all channels. |
|
zigbee_sniff |
This module sniffs Zigbee communications on a given channel. |
The following modules allows to manipulate Infrared Radiations signals :
Name |
Description |
Documentation |
|---|---|---|
ir_info |
This module displays useful informations about a given interface. |
|
ir_sniff |
This module sniffs the Infrared Radiations signals. |
|
ir_inject |
This module injects the Infrared Radiations signals. |
Modes¶
Mirage provides two main interfaces :
Getting started¶
Configuring and running a module is quite simple.
First of all, you need to launch Mirage :
mirage
You can use the list command in order to list the existing modules :
~~> list
┌Modules───────┬────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Name │ Type │ Description │
├──────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ble_hijack │ attack │ Hijacking module for Bluetooth Low Energy Connections │
│ ble_pair │ action │ Pairing module for Bluetooth Low Energy devices │
│ ble_adv │ spoofing │ Spoofing module simulating a Bluetooth Low Energy advertiser │
│ ble_mitm │ attack │ Man-in-the-Middle module for Bluetooth Low Energy devices │
│ ble_adb │ monitoring │ Sniffing module monitoring an HCI Android log │
│ ble_sniff │ sniff │ Sniffing module for Bluetooth Low Energy devices │
│ bt_scan │ scan │ Scan module for Bluetooth Devices │
│ ble_scan │ scan │ Scan module for Bluetooth Low Energy devices │
│ ble_discover │ discover │ Discovery module for Bluetooth Low Energy ATT / GATT layers │
│ ble_jam │ attack │ Jamming module for Bluetooth Low Energy advertisements and connections │
│ ble_connect │ action │ Connection module for Bluetooth Low Energy devices │
│ bt_info │ info │ Information module for Bluetooth interface │
│ ble_slave │ spoofing │ Spoofing module simulating a Bluetooth Low Energy slave │
│ ble_crack │ bruteforce │ Enumerates all possible values of PIN in order to find the Temporary Key │
│ ble_master │ spoofing │ This module permits the User to interact with Bluetooth Low Energy slaves │
│ ble_info │ info │ Information module for Bluetooth Low Energy interface │
└──────────────┴────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
If you want to load the module ble_info from the Command-Line Interface, just type the following command :
~~> load ble_info
[INFO] Module ble_info loaded !
<< ble_info >>~~>
As you can see, the prompt has changed, indicating that a module is currently loaded.
You can use the args command in order to display the input parameters and their current values :
<< ble_info >>~~> args
┌ble_info───┬───────┐
│ Name │ Value │
├───────────┼───────┤
│ INTERFACE │ hci0 │
└───────────┴───────┘
You can modify a parameter’s value using the command set :
<< ble_info >>~~> set INTERFACE microbit0
Finally, you can run the module by typing the run command :
<< ble_info >>~~> run
If you want to run this module directly from the bash environment, you can type the following command :
mirage ble_info INTERFACE=microbit0